
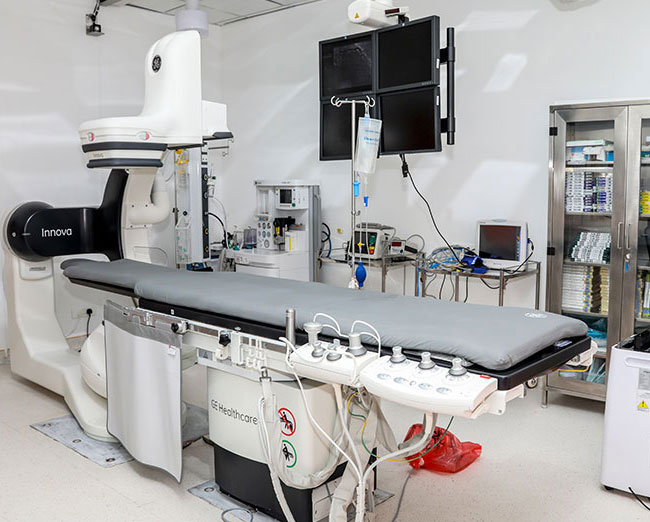
The department of Cardiac Sciences at the SUHRC offers the latest in Cardiology & Cardiac Surgical services, supported by a state-of-the art infrastructure that includes the most recent Cath lab & modular operation theatres. Here, you will find a pleasing blend of knowledgeable experts, modern technology, hi-tech infrastructure and a serene, pollution-free environment, each of which facilitate early patient recovery.
Apart from delivering focused patient care, the SUHRC places a strong emphasis on disease prevention & healthy life styles. Furthermore, informational initiatives like the SUHRC Knowledge Series aim at increasing public awareness about common health conditions and dispelling myths.
Our holistic approach to heart ailments is underlined by our comprehensive services that include both treatment and prevention.
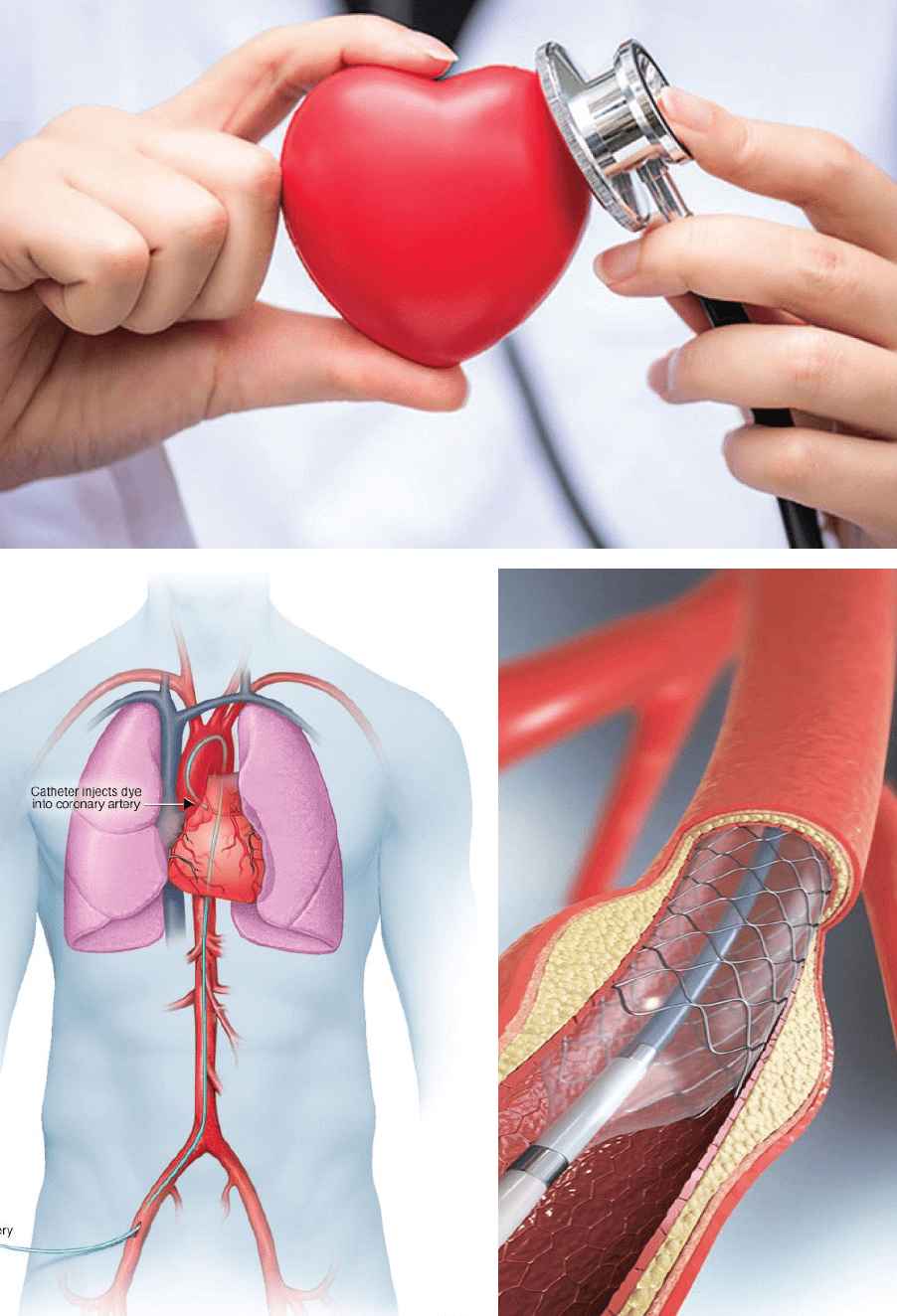
Coronary angiography is a test used to find out how much narrowing there is in your arteries. Learn what to expect and when you might get a stent.
Angiography is an imaging test that uses X-rays to view your body’s blood vessels. The X-rays provided by an angiography are called angiograms. This test is used to study narrow, blocked, enlarged, or malformed arteries or veins in many parts of your body, including your brain, heart, abdomen, and legs.
A coronary angiogram is an X-ray of the arteries in the heart. This shows the extent and severity of any heart disease, and can help you to figure out how well your heart is working. With this information, you and your doctor can talk through your treatment options. These may include angioplasty (stents), bypass graft surgery or medications.
It is performed to diagnose heart defects present from birth (congenital heart defects). It is also used as part of some procedures to treat heart disease which include closure of holes in the heart, ballooning and stenting of coarctation of aorta and fixing other congenital defects. COA - Coarctation of the aorta is a narrowing of the aorta, the major blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the body. This narrowing causes the left side of the heart to work harder to pump blood through the aorta.
Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Intervention is a minimally invasive technique used to treat patients with long standing blockages. These blockages are a result of severe build-up of fatty deposits/plaque within the arteries (atherosclerosis) and are one of the complications from CAD. CTO PCI is a complex procedure that requires expert care from very highly experienced cardiologists and are recognized internationally as pioneers in the field.
Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart arteries. Angioplasty involves temporarily inserting and inflating a tiny balloon where your artery is clogged to help widen the artery. Angioplasty is often combined with the permanent placement of a small wire mesh tube called a stent to help prop the artery open and decrease its chance of narrowing again. Some stents are coated with medication to help keep your artery open (drug-eluting stents), while others are not (bare-metal stents).
Angioplasty can improve symptoms of blocked arteries, such as chest pain and shortness of breath. Angioplasty can also be used during a heart attack to quickly open a blocked artery and reduce the amount of damage to your heart.
A renal angiogram is an imaging test to look at the blood vessels in your kidneys and to detect any signs of blockage or abnormalities affecting the blood supply to the kidneys.
A peripheral angiogram is a test that help your doctor find narrowed or blocked areas in one or more of the arteries that supply blood to your limbs. The test is also called a peripheral arteriogram.
The emergence of new diagnostic modalities has provided our clinicians with adjunctive physiologic and image-based data to help them formulate treatment strategies and they are highly experienced and pioneers in the field. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) can predict whether percutaneous intervention will benefit a patient. Intravascular ultrasonography (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) are intracoronary imaging modalities that facilitate the anatomic visualization of the vessel lumen and characterize plaques.
An electrophysiology study (EPS) is a study that helps doctor to assess abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) through electrical system.
This test is performed by inserting thin electrodes which measure heart electrical signals. These signals stimulate the heart tissue to record the cause of abnormal heart rhythm.
EPS is used to check from where abnormal heart rhythm is coming from & how well the medicines prescribed are working on the arrhythmia.
Radio frequency ablation (RFA) is a procedure used to put the heart back into normal rhythm. During RFA, a thin wire sends heat to fix problem areas that cause abnormal heart beats. Medicines can also be used to put the heart back into normal rhythm.
Temporary pacemaker (TP) are used in the emergency treatment of patients with severe bradyarrhythmia. They are often used in emergency situations like Heart Block and also for older patients in poor general condition who are hemodynamically unstable. It is also used when the condition is temporary and when a permanent pacemaker is not required.
There are two types of CRT Devices. Depending on your heart failure condition, a Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P) or a Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) may be indicated
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a small electronic device installed inside the chest to prevent sudden death from cardiac arrest due to life threatening abnormally fast heart rhythms (tachycardia’s & fibrillation). The ICD is capable of monitoring the heart rhythm. ICDs have a role in preventing cardiac arrest in high-risk, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist, particularly a cardiac electrophysiologist to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients.
Percutaneous Balloon Pulmonary Valvuloplasty (BPV) is the mainstay of treatment for significant pulmonary stenosis with doming leaflets. Congenital pulmonary stenosis is a health problem present from birth. It’s when the pulmonary valve in your heart doesn’t fully open. Balloon valvuloplasty is a type of procedure that aims to fix this problem. It does so without the need for open heart surgery.
Balloon Mitral Valvotomy (BMV) is used to increase the opening of a narrowed (stenotic) valve and is the procedure of choice for severe mitral stenosis (MS) when valve morphology is feasible. This balloon valvotomy procedure can be performed on the mitral, tricuspid, aortic or pulmonary valves. The procedure lasts about 1 hour.
Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty (BAV) is a percutaneous treatment option for severe, symptomatic aortic stenosis. It stretches the aortic valve to improve the symptoms of aortic stenosis. Due to early restenosis and failure to improve long term survival, BAV is considered as palliative measure in patients who are not suitable for open heart surgery due to increased perioperative risk.
Closure devices are used to close a defect or an opening between the right and left sides of the heart. Some of these birth defects are located in the wall (septum) between the chambers of the heart
Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) closure is now a widely recognized alternative to surgical closure for suitable secundum ASDs.
A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a hole between the two lower chambers of the heart. It is a common congenital heart defect in both children and adults. Device closure of ventricular septal defects is safer and feasible alternative to surgical closure.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart condition that affects blood flow in your child’s heart. Because the blood flow isn’t efficient, your child’s heart and lungs have to work harder. When the ductus arteriosus does not close, oxygen-rich blood from your infant’s aorta mixes with oxygen-poor blood from the pulmonary artery, causing strain on the heart and lungs. If untreated, PDA can lead to difficulty breathing, chronic respiratory infections and heart failure. The most common form of intervention for older infants and children is “device closure” in the cardiac catheterization laboratory.
Coil embolization is a minimally-invasive procedure that stops blood flow to an aneurysm by placing a small metal coil inside it. In this procedure, your doctor will insert a catheter into a blood vessel in your groin and guide it to the aneurysm.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement/ Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation is a well proven procedure for aortic valve replacement in people who are considered as high risk patients for Open Heart Surgery. In this procedure, a new aortic valve is fixed without removing the old, damaged valve with the help of a specialized catheter through a process similar to stenting. A new artificial valve wedges into the place of the older aortic valve.
Surgery to repair or replace aortic aneurysms and aortic dissections.
Surgery to repair or replace an aortic valve that is not working correctly.
A surgical procedure to correct irregular heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
Corrective surgery to fix or treat a genetic heart defect.
A surgical procedure in which the blocked portion of the coronary artery is bypassed with another piece of blood vessel.
A mechanical device which aids in the pumping function of the blood.
A technique that provides the heart with a more normal shape after a heart attack, allowing it to pump blood more efficiently.
A surgical treatment option that removes a portion of the enlarged heart wall.
A procedure used to relieve severe angina or chest pain in patients who aren’t candidates for bypass surgery or angioplasty.
Heart valve surgery used to repair or replace diseased heart valves.
Minimally invasive heart surgery involves making small incisions in your chest to reach the heart, rather than cutting through the breastbone, as is done in open-heart surgery. Minimally invasive heart surgery can be performed to treat a variety of heart conditions. Compared with open-heart surgery, this type of surgery might mean less pain and a quicker recovery for many people.
Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery is the latest technique to do heart surgeries. And for many heart problems, MICS gives more convenience and effectiveness to the surgeons.
These are some of the benefits that Minimally Invasive Heart Valve Surgery offers to the patients
Heart ailments are often thought of as an affliction of adults. But unfortunately, children too suffer from, for no fault of their own, serious, and even life threatening cardiac conditions. From accurate and timely diagnosis to appropriate and proficient treatment, the paediatric cardiology unit provides end-to-end cardiac care right from 18 weeks of gestation. These include both care and correction for congenital heart diseases like
as well as treatment for acquired cardiac conditions like
Our paediatric cardiac care facility also provides the full spectrum of paediatric electrophysiology services including
Emergency redo surgery is rare, but may be required in patients with conditions such as endocarditis, unstable angina and acute aortic dissection.
Effective treatment is entirely dependent on efficient diagnosis. So, we stress on comprehensive cardiac imaging services. We provide all services including